Daliborlev (CC), Flickr
Daliborlev (CC), Flickr
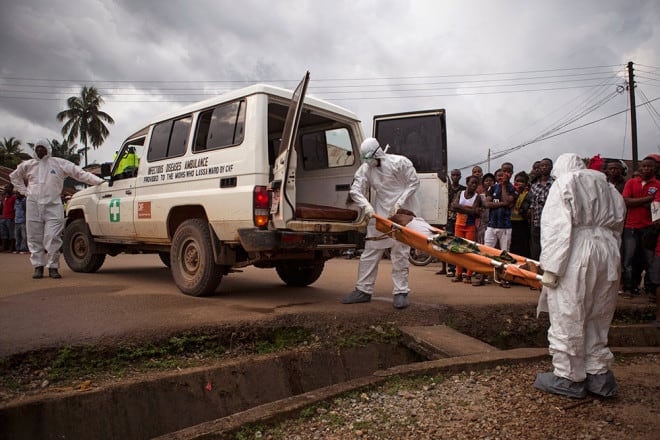
Since last week, there has been some good news on the Ebola front: a suggestion that the epidemic in Liberia is beginning to slow down, with fewer new cases reported. At the same time, there is a new outbreak in Sierra Leone, in a part of the country that thought it had beaten the disease and then self-quarantined to keep it at bay. So it is probably too soon to hope that the entire international outbreak is on its way to being extinguished.
At the same time, two major international medical meetings happening this week have allowed researchers to discuss the newest reports from the field — but not with equal success. The annual meeting of the American Society of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene, the largest medical society devoted to diseases such as Ebola, lost a significant number of attendees when the conference’s host state, Louisiana, threatened to forcibly quarantine anyone traveling from a country experiencing Ebola, whether or not that person had been exposed. Meanwhile, Vienna, Austria had no such qualms, and so the International Meeting on Emerging Diseases and Surveillance proceeded without any difficulties, allowing physicians and epidemiologists fresh from the Ebola zone to share reports.
It’s from that second meeting that this week’s news comes. Oyewale Tomori, president of the Nigerian Academy of Science and a leader of the World Health Organization’s Ebola response in 1995, used the IMED podium to deliver a stinging critique of the behavior of African governments during the current crisis, charging that internal corruption has crippled the continent’s ability to fight its own disease battles.

 Tanya Bindra/AP
Tanya Bindra/AP